29.11.2023
15 minutes of reading
 Andreas Ehinger
Andreas Ehinger
Doctoral Program Director
“The doctorate suffers from a poor image throughout virtually the whole of French society.” This warning, recently delivered by the French National Research and Technology Association (ANRT), is accompanied, in the same report, by another observation: “The doctorate is strategic, a vital asset within the context of unparalleled international competition for talent.” The combination of these two alarming observations for France gives rise to a powerful appeal “For a major national plan to support the doctorate”.
At IFP Energies nouvelles, we have always believed in the vital contribution made by our doctoral students to scientific advances and the expansion of cutting-edge knowledge in our research fields, as well as in the need to thoroughly train our doctoral students and prepare them to take responsibilities in a broad range of activities and economic sectors. Our doctoral training program, targeting doctoral students as well as their supervisors, reflect this ambition.
The scientific excellence of our doctoral students is recognized via the numerous prizes and awards they are given by their peers for their research, and by the Yves Chauvin Prize for the best IFPEN thesis. In this issue, you can read about the themes submitted to the Scientific Committee for selection this year, starting with that of award winner Alexandre Delarouzée.
Yves Chauvin Prize: Metabolic engineering at the heart of bio-based processes
Within the context of the energy transition, new bioprocesses are emerging as substitutes for processes using fossil resources. For example, Clostridium acetobutylicum is a microorganism capable of converting the large variety of sugars derived from lignocellulosic biomass into a raft of bio-based substances, via fermentation. This makes it a potential candidate for producing biofuels and/or chemical intermediates that can be used by industry....
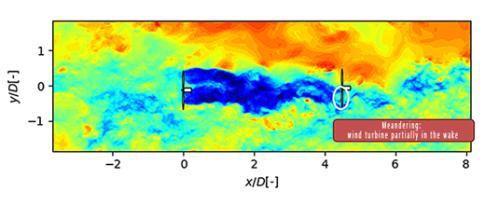
Modeling wind turbine wake: a question of atmosphere!
In the wake zone located behind each wind turbine, wind velocity is reduced and turbulence increased. This results in a reduction in the lifespan of machines located downstream as well as a decrease in a windfarm’s overall electricity production. To limit these effects and help optimize the siting of turbines on windfarms, analytical wake models exist in the literature but they incorporate numerous simplifying hypotheses concerning wind turbines and their environment...
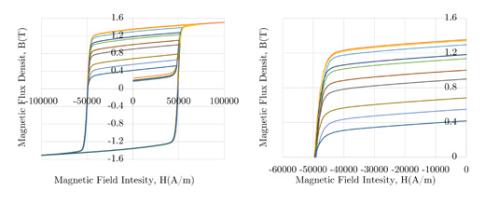
Magnets for future generations of electric vehicles
Permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM) are a reference technology for electric vehicle propulsion. However, their large-scale deployment is subject to the constraints associated with magnets: the capacity to obtain resources as well as the environmental challenges related to mining, recycling and refining. In addition, PMSMs often require flux-weakening1 strategies in order to operate at high speeds, which can result in energy losses...
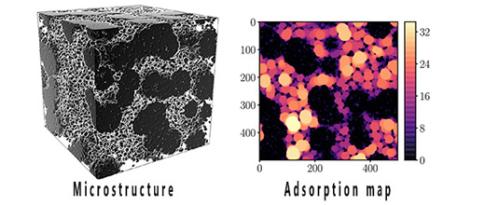
Digital porous materials: from the virtual to very real interest!
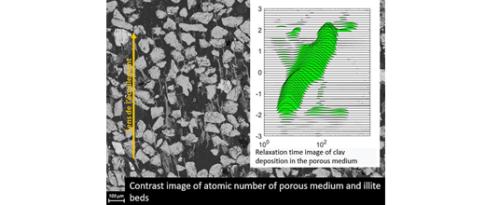
While macroscopic models combined with experimental analysis of porosity are well established for geometrically simple pores, hierarchized and disordered microstructures defy existing frameworks and call into question conventional interpretations. We proposed a digital framework to help overcome this challenge, taking into account morphology, connectivity and pore size distribution...
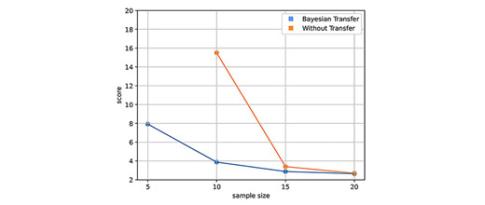
Transfer learning for process optimization
IFPEN is a global leader in the development of catalysts and processes for clean fuel production. For these processes themselves to be eco-efficient1, it is necessary to optimize the coupling of catalysts with the operating conditions, as a function of the feedstocks used and the target specifications for the refined products. It is therefore useful to be able to draw on predictive models for the performance achieved, and machine learning can help improving these models...
Deep learning in the field of thermodynamics
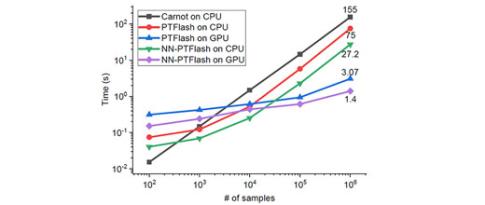
Reactive fluid transport simulation has multiple applications - flows in porous media, combustion, process engineering - and requires thermodynamic equilibrium calculations (also knows as “flash” calculations). However, these calculations can take a long time and, as they are involved in large numbers in the simulations carried out, in practice they limit the latter to systems containing few chemical species or to restricted time and space scales...
Clogging is a major challenge for geothermal energy
In a porous geological structure, the flow of a geothermal fluid carries along solid particles for which the rock acts as a filter. The capture of these particles causes the permeability of the porous medium to gradually decrease, which can lead to a drastic reduction in injectivity and eventual failure of the industrial operation...