15.09.2023
15 minutes of reading
 Richard Tilagone
Richard Tilagone
Director, Mobility & Systems Division
 Christian Angelberger
Christian Angelberger
Scientific Assistant Director, Mobility & Systems Division
The mobility of goods and people is a key component in the development of modern societies, and ensuring its sustainability requires reducing the associated energy consumption while limiting its impact on the environment and health. Developing technological solutions for a more sustainable and socially acceptable mobility is one of the raisons d'être and the driving force of the "Mobility & Systems" Division.
To this end, we contribute to the development of innovative powertrain systems, whether electric, based on internal combustion or hybrid, for low-carbon, energy-efficient mobility with low or zero emissions. Our technological R&I is based on a rich fundamental foundation, combining the development of methods and tools for the design of complex mechatronic systems, simulation techniques and software ranging from system-level to multidimensional, and advanced measurement techniques and equipment. Our points of differentiation stem from our ability to implement them in a design approach that is equally multi-physics (solid and fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, chemical kinetics, electromagnetism), multi-scale (from component to system) and multi-objective (energy efficiency, emissions reduction, mechanical, thermal and chemical strength and durability).
The field of mobility, until very recently focused on fossil-fuel-powered internal combustion engines, has undergone a profound transformation, the scope of which is still difficult to grasp. As such, while electrification will undoubtedly represent one of the major mobility solutions, it seems established that it alone will not be able to meet the complex challenges of mobility, and that complementary approaches based on the consumption of decarbonated fuels and energies will therefore be part of the scope of solutions.
To keep pace with these changes, our Research Division has launched a profound evolution of its research themes. In this context, our originality lies in our ability to invest in electrification-related domains, while at the same time developing our historical focus on combustion and effluent after-treatment, thereby enabling us to offer an innovative and differentiating approach in a highly competitive field.
This special issue illustrates how some of our fundamental research activities feed into and enrich our R&I work in the service of sustainable mobility. We hope that it will bring to light the major changes that have taken place within the “Mobility and Systems” Division, and we invite you to get in touch with the colleagues who will share with you our ambitions for the short, medium and long terms.
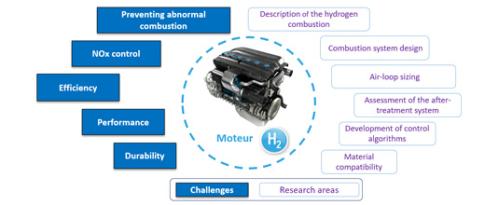
Hydrogen: two complementary paths to sustainable mobility
The goal of carbon neutrality by 2050 requires a drastic reduction of transport-related CO2 emissions, which alone account for over 30% of global CO2 emissions. For road transport, decarbonization is expected to be partly based on the roll-out of battery-powered electric vehicles. However, the constraints imposed by this solution...
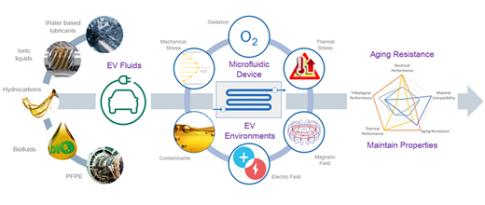
Ageing of technical fluids in multifunctional environments
By combining battery, electric machine, power electronics and mechanical transmission, the electric vehicle is an example of an application that combines a range of constraints for the formulation of technical fluids. In recent years, there has been renewed interest in the study of the latter for the transport sector...
Road transport emissions: integrated research for air quality!
According to the WHO, 7 million premature deaths worldwide each year are linked to poor air quality, a problem to which road transport makes a significant contribution. Thanks to regulatory and technological developments, as well as the renewal of the vehicle fleet, emissions from this sector have certainly been falling in recent years. However, it remains a major contributor to the deterioration of air quality...
Electrical machines: Design, optimization, control and diagnosis
Like all sectors concerned by electrification, the transport sector requires the design of high-performance, efficient electrical systems that respond to multiple constraints, such as cost and compactness. In this context, optimisation has become an essential step in the design process of these systems, particularly for electrical machines...
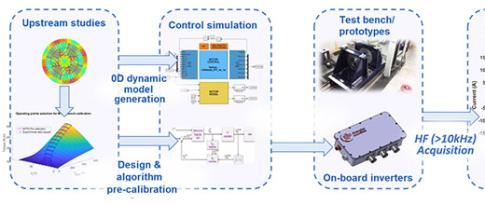
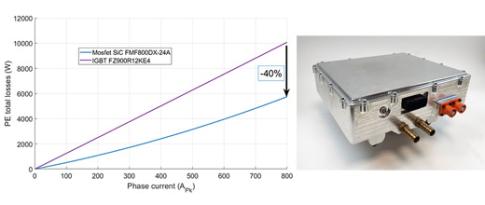
Power electronics at the heart of electric mobility challenges
In the case of electrified vehicles, whether battery-powered (electric or hybrid) or powered by fuel cells (FC), power electronics (PE) converters play a major role, as they are used for a variety of functions. For example, they are used to drive electric motors, manage on-board energy or control traction battery recharging...
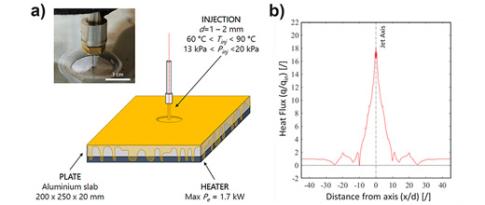
Electric motor: oil cooling is more difficult
The thermal management of electric motors is an essential element in competitive low-carbon mobility, since more efficient cooling not only increases motor performance density (power or torque by mass), but also improves operational reliability by preventing deterioration phenomena (such as demagnetization)...